Hermit Crab Anatomy
This page is all about the parts that make up this fascinating creature.
 CLASSIFICATION CLASSIFICATION
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: Crustacea
Class: Malacostraca
Order: Decapoda
Infraorder: Anomura
Family: Coenobitidae
Genus: Coenobita
Species: C. clypeatus
|
|

|
Coenobita clypeatus: This species is commonly referred to as the purple pincher crab, PP, or Caribbean crab and is indigenous to southern Florida and found throughout the Caribbean islands.
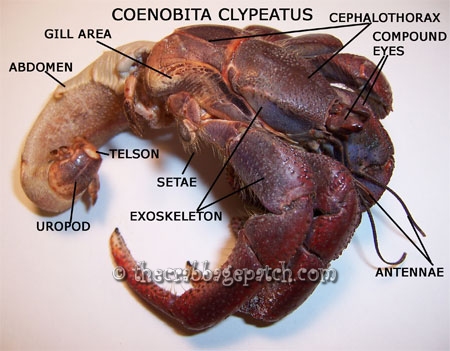
Antennae: two pairs of sensory organs used to gather information regarding a hermit crabs surroundings. Antenna - the longer outer pair often referred to as "feelers" used to touch and feel what is in the crabs path. Antennule - the inner "bent" pair which enable the crab to taste and smell (this is the pair that you touch gently with food when beginning to hand feed your crab with The Hermit Crab Patch Feeder Spoon).
Compound Eyes: eyes comprised of faceted lenses which are especially adept at picking up fine movements. Eyes are located on movable stalks.
Maxillipeds: also referred to as mouthparts. 3 pairs of appendages used to move food into the crabs mouth as well as for grooming.
Exoskeleton: the hard outer, protective layer which must be shed as the crab grows.
Chelipeds: claws used to grasp and pinch. Large claw - the larger left claw which is primarily used for defense and to effectively seal off the opening in a properly fitting shell. Small claw - the smaller right claw which is most often used in feeding and scooping water up to the crabs maxillipeds.
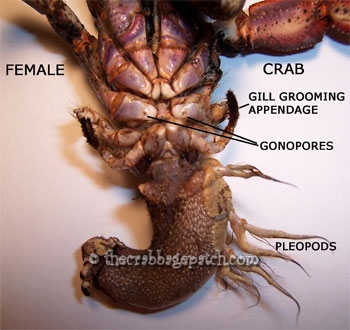
Pereiopods: legs. Technically hermit crabs have 10 legs including the chelipeds. 2nd &3rd pair - walking legs used for movement. Gonopores are located at the base of the 3rd pair of legs on a female. 4th pair - stubby looking legs used to move in and out of shell. 5th pair - gill grooming appendages that end in pinchers for cleaning the gills and removing excrement from the shell. Male crabs have tufts of hair concealing openings at the base of the 5th pair of legs.
Cephalothorax: the head and back region on a hermit crab.
Carapace: the hard outer shield comprised of exoskeleton covering the cephalthorax.
Setae: sensory hairs found on the exoskeleton.
Gills: organs by which the crab "breathes". They have modified gills located between the 4th and 5th periopods housed in the brachial chamber which must be kept moist to function.
Abdomen: or tail as it is commonly called. The soft portion of the crab protected within a shell and contains the digestive and reproductive organs.
Pleopods: feathery looking appendages located on the left side of a female's abdomen that are used for carrying eggs.
Uropods: appendages located at the tip of the abdomen that are used to secure the crab within its shell.
Telson: the tip of the tail ending in the anus.
|

|
|